Treatment of shoulder tendonitis or tendon tears
Causes of shoulder tendonitis and tendon tears
There are many reasons that may lead to shoulder tendonitis or tendon tears, the most prominent of which are:
Repetitive stress: Excessive use of the shoulder in daily or sports activities that require constant lifting of the arm may lead to tendonitis, especially in athletes and workers in jobs that require repetitive movements.
Aging: As you age, the tendons weaken and become less flexible, which increases the likelihood of them becoming inflamed or torn.
Sudden injuries: Falls or sudden injuries may lead to a tear in the shoulder tendons, especially when practicing sports that involve quick movements or jumps.
Incorrect postures: Sitting or standing in incorrect positions for long periods of time can strain the tendons and muscles, causing inflammation or weakness.
Symptoms of shoulder tendonitis or rupture
Symptoms range from mild to severe pain, and include:
- Pain in the shoulder, which increases with movement or when raising the arm.
- Difficulty moving the shoulder normally.
- Weakness in the affected arm.
- Swelling or redness around the shoulder in the case of acute inflammation.
- Crackling or rattling sounds when moving the shoulder.
- Methods of treating shoulder tendonitis or rupture
Treatment methods vary between conservative treatment and surgical treatment, and the choice depends on the severity and type of injury.
First: Conservative treatment
Rest and avoid strenuous activities: The patient is advised to rest and avoid activities that increase pain and stress on the shoulder, especially activities that require raising the arm.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy is one of the most prominent methods of treatment to control pain and strengthen the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint. This includes exercises to increase the flexibility and strength of the tendons and reduce pressure on them.
Ice and heat therapy: Using ice helps reduce pain and swelling, while heat can help relax muscles and improve blood flow to the affected area.
Anti-inflammatory medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen help relieve pain and reduce swelling.
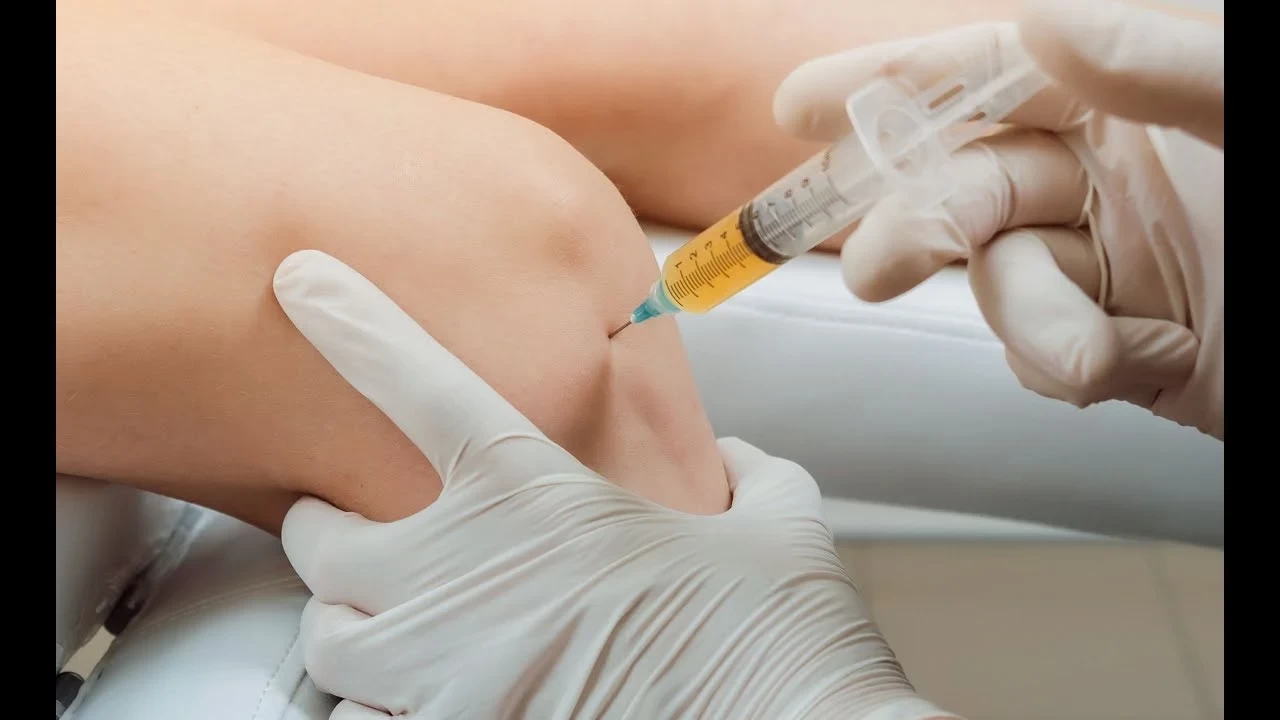
Cortisone injections: In some cases, the doctor may suggest injecting cortisone directly into the shoulder to relieve pain and reduce inflammation, but they should be used with caution to avoid complications.
Second: Surgical treatment
If conservative treatment fails or in the case of a complete tear in the tendons, the doctor may resort to surgical treatment. Surgical options vary, including:
Arthroscopic surgery: It is considered one of the most commonly used surgical methods because it requires only small openings, and through it, damaged or torn tendons are repaired using a camera and precise tools.
Open surgery: It is used in cases that require larger repairs or if the tears are severe, where the shoulder is opened and the tendons are reached to repair them.
Tendon reconstruction: In some advanced cases, a procedure may be performed to reconstruct the tendon using tissue taken from another part of the body. This option is usually used in cases of severe rupture or if the tendon is damaged beyond repair.
Recovery period and patient advice
After treatment, whether conservative or surgical, the recovery period requires some time and commitment to a rehabilitation program determined by the doctor. The recovery period may take from several weeks to several months depending on the severity of the injury and the type of treatment. Tips that help speed up recovery include:
Commit to daily exercises to strengthen the muscles and maintain shoulder flexibility.
Avoid sudden movements or strenuous activities until full recovery.
Follow the instructions of the doctor and physical therapist carefully.
Conclusion
Inflammation or rupture of the shoulder tendons is one of the injuries that greatly affects the patient's quality of life, as it may limit his ability to perform daily and sports activities. Treatment methods vary between conservative and surgical treatment, and modern medical developments, especially in arthroscopic surgery, provide the patient with the opportunity to recover faster and safer. By adhering to rest, physical therapy, and avoiding stress, the patient can regain shoulder function, eliminate pain, and return to normal activities.