Treatment of lateral ligament tears in the knee
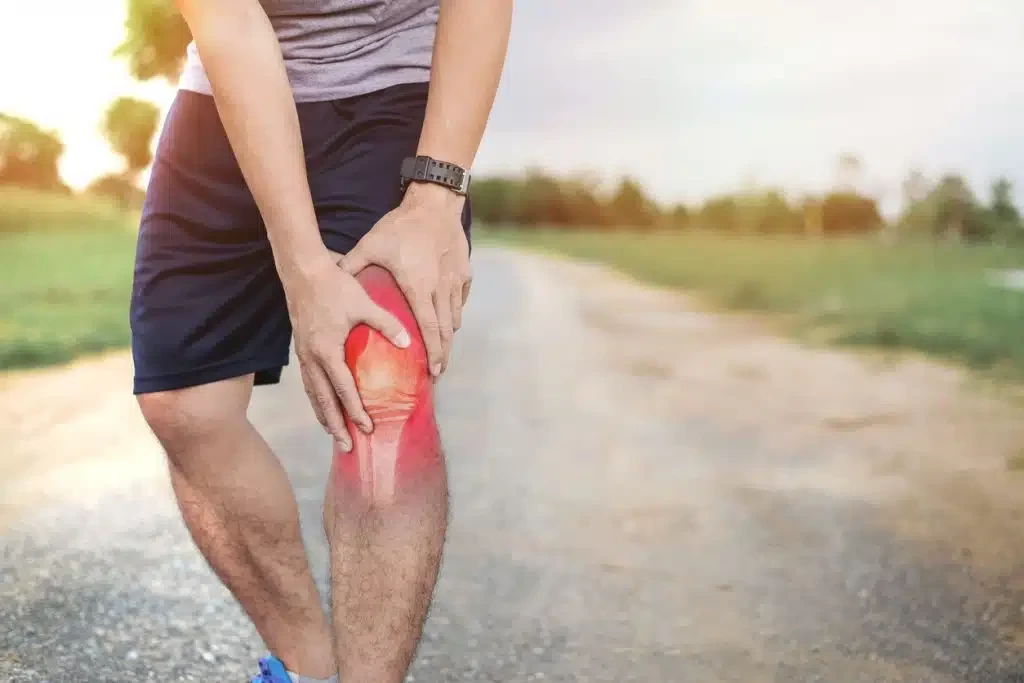
Causes of lateral ligament tears in the knee
A lateral ligament tear usually occurs as a result of a direct injury or sudden movement, and the main causes vary between:
Sports injuries: Sports that require physical contact or a quick change in direction such as football, basketball, and tennis are among the most prominent causes of lateral ligament tears.
Fall accidents: Fall accidents, especially falling on the side of the knee, can lead to lateral ligament tears.
Traffic accidents: Sudden shocks to the knee can cause severe injuries, including lateral ligament tears.
Sudden twisting: Sudden and strong twists during movement or due to tripping can cause a tear in the collateral ligaments of the knee.
Symptoms of a torn collateral ligament of the knee
Symptoms of a torn collateral ligament vary depending on the severity of the tear, but common symptoms include:
- Severe pain in the area of the injured ligament.
- Swelling around the knee joint.
- Instability in the knee and difficulty moving it.
- Difficulty putting weight on the injured knee.
- Bruising and discoloration of the skin around the knee after a period of injury.
- Diagnosis of a torn collateral ligament
Diagnosis of a torn collateral ligament depends on a comprehensive evaluation of the injury, including:
Physical examination: The doctor evaluates the range of motion and stability of the knee through a physical examination of the knee.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI is one of the most important tests that helps determine the degree of the tear and to see if there are other injuries to the knee, such as a torn cartilage.
X-rays: X-rays can be used to rule out associated bone fractures.
Treatment methods for lateral ligament tears of the knee
Treatment methods vary depending on the severity of the tear and the degree of ligament injury, and are generally divided into conservative treatment and surgical treatment.
First: Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment is usually used in cases of partial tears or minor injuries, and includes:
Rest and avoidance of strenuous activities: It is recommended to rest and avoid putting weight on the injured knee to give it the necessary time to recover.
Ice therapy: Applying ice to the knee helps reduce pain and swelling, especially in the first days after the injury.
Brace or compression bandage: A knee brace or compression bandage can be used to stabilize the joint and maintain its stability during the recovery period.
Physiotherapy: After reducing swelling and pain, a physical therapy program is started to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee and improve stability. Physiotherapy exercises include strengthening exercises and exercises to improve range of motion.
Anti-inflammatory medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen help relieve pain and reduce swelling.
Second: Surgical treatment
In cases where the tear is severe or when the patient does not respond to conservative treatment, surgical intervention may be required. Surgical treatment includes:
Colateral ligament repair: If the tear allows for repair, the injured ligament is fixed using sutures or supports to achieve stability.
Ligament reconstruction: If the ligament is completely torn, it may be necessary to reconstruct the ligament using tissue taken from another part of the body, such as the hamstring tendon or thigh muscle.
Arthroscopic surgery: In some cases, arthroscopic surgery can be used to treat minor tears, where a small camera and surgical tools are inserted through small incisions, which helps reduce the recovery period.
Recovery period and advice for the patient
The recovery period varies depending on the severity of the injury and the type of treatment used. After surgery, the patient needs to adhere to a rehabilitation program to help restore strength and full movement of the knee. Advice to follow during the recovery period includes:
Commit to rest and avoid strenuous activities until the doctor allows them to return gradually.
Regular physical therapy sessions to enhance muscle strength and support the knee.
Avoid putting weight on the injured knee as directed by your doctor.
Follow a healthy diet to help speed up the recovery process.
Conclusion
Treating lateral ligament tears of the knee is a medical challenge, as it requires accurate diagnosis and determining the appropriate treatment plan according to the severity of the injury. Conservative and surgical treatment, in addition to adherence to physical therapy and preventive advice, contribute to restoring knee function and improving the patient's quality of life, enabling him to return to his daily and sports activities normally and safely.